Diabetes Treatment
 Diabetes, often referred to by doctors as diabetes mellitus, describes a group of metabolic diseases in which the person has high blood glucose (blood sugar), either because insulin production is inadequate, or because the body's cells do not respond properly to insulin, or both. Patients with high blood sugar will typically experience polyuria (frequent urination), they will become increasingly thirsty (polydipsia) and hungry (polyphagia).
Diabetes, often referred to by doctors as diabetes mellitus, describes a group of metabolic diseases in which the person has high blood glucose (blood sugar), either because insulin production is inadequate, or because the body's cells do not respond properly to insulin, or both. Patients with high blood sugar will typically experience polyuria (frequent urination), they will become increasingly thirsty (polydipsia) and hungry (polyphagia).
Fast facts on diabetes
Here are some key points about diabetes. More detail and supporting information is in the main article.
- Diabetes is a long-term condition that causes high blood sugar levels.
- Type 1 Diabetes - the body does not produce insulin. Approximately 10% of all diabetes cases are type 1.
- Type 2 Diabetes - the body does not produce enough insulin for proper function. Approximately 90% of all cases of diabetes worldwide are of this type.
- Gestational Diabetes - this type affects females during pregnancy.
- The most common diabetes symptoms include frequent urination, intense thirst and hunger, weight gain, unusual weight loss, fatigue, cuts and bruises that do not heal, male sexual dysfunction, numbness and tingling in hands and feet.
- If you have Type 1 and follow a healthy eating plan, do adequate exercise, and take insulin, you can lead a normal life.
- Type 2 patients need to eat healthily, be physically active, and test their blood glucose. They may also need to take oral medication, and insulin to control blood glucose levels.
- As the risk of cardiovascular disease is much higher for a diabetic, it is crucial that blood pressure and cholesterol levels are monitored regularly.
- As smoking might have a serious effect on cardiovascular health, diabetics should stop smoking.
- Hypoglycemia - low blood glucose - can have a bad effect on the patient. Hyperglycemia - when blood glucose is too high - can also have a bad effect on the patient.
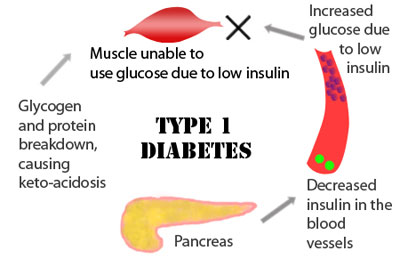
Type-1 Diabetes Mellitus
The body does not produce insulin. Some people may refer to this type as insulin-dependent diabetes, juvenile diabetes, or early-onset diabetes. People usually develop type 1 diabetes before their 40th year, often in early adulthood or teenage years.
Type 1 diabetes is nowhere near as common as type 2 diabetes. Approximately 10% of all diabetes cases are type 1.
Patients with type 1 diabetes will need to take insulin injections for the rest of their life. They must also ensure proper blood-glucose levels by carrying out regular blood tests and following a special diet.
Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus
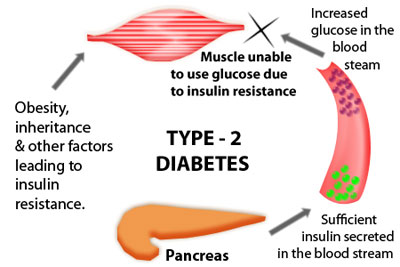 Some people may be able to control their type 2 diabetes symptoms by losing weight, following a healthy diet, doing plenty of exercise, and monitoring their blood glucose levels. However, type 2 diabetes is typically a progressive disease - it gradually gets worse - and the patient will probably end up have to take insulin, usually in tablet form.
Some people may be able to control their type 2 diabetes symptoms by losing weight, following a healthy diet, doing plenty of exercise, and monitoring their blood glucose levels. However, type 2 diabetes is typically a progressive disease - it gradually gets worse - and the patient will probably end up have to take insulin, usually in tablet form.
Overweight and obese people have a much higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes compared to those with a healthy body weight. People with a lot of visceral fat, also known as central obesity, belly fat, or abdominal obesity, are especially at risk. Being overweight/obese causes the body to release chemicals that can destabilize the body's cardiovascular and metabolic systems.
Being overweight, physically inactive and eating the wrong foods all contribute to our risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Drinking just one can of (non-diet) soda per day can raise our risk of developing type 2 diabetes by 22%, researchers from Imperial College London reported in the journal Diabetologia. The scientists believe that the impact of sugary soft drinks on diabetes risk may be a direct one, rather than simply an influence on body weight.
The risk of developing type 2 diabetes is also greater as we get older. Experts are not completely sure why, but say that as we age we tend to put on weight and become less physically active. Those with a close relative who had/had type 2 diabetes, people of Middle Eastern, African, or South Asian descent also have a higher risk of developing the disease.
Men whose testosterone levels are low have been found to have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Researchers from the University of Edinburgh, Scotland, say that low testosterone levels are linked to insulin resistance.
Symptoms
Here is a list of the most common diabetes symptoms:
- Frequent urination
- Disproportionate thirst
- Intense hunger
- Weight gain
- Unusual weight loss
- Increased fatigue
- Irritability
- Blurred vision
- Cuts and bruises don't heal properly or quickly
- More skin and/or yeast infections
- Itchy skin
- Gums are red and/or swollen - Gums pull away from teeth
- Frequent gum disease/infection
- Sexual dysfunction among men
- Numbness or tingling, especially in your feet and hands
Treatments
As well as making lifestyle changes, people with diabetes often need additional treatments such as medication to control their diabetes, blood pressure and blood fats. This section helps to explain more about some of the more common treatments for people with diabetes.
Remember that the information in this section is general information and it is important that you discuss any concerns or problems you may have with your medications and treatments with your healthcare team.
Medication is not a substitute for following a healthy diet and taking regular physical activity – you will still need to carry on with this.
- Diabetes medication
- Insulin
- Islet cell transplants





 Diabetes, often referred to by doctors as diabetes mellitus, describes a group of metabolic diseases in which the person has high blood glucose (blood sugar), either because insulin production is inadequate, or because the body's cells do not respond properly to insulin, or both. Patients with high blood sugar will typically experience polyuria (frequent urination), they will become increasingly thirsty (polydipsia) and hungry (polyphagia).
Diabetes, often referred to by doctors as diabetes mellitus, describes a group of metabolic diseases in which the person has high blood glucose (blood sugar), either because insulin production is inadequate, or because the body's cells do not respond properly to insulin, or both. Patients with high blood sugar will typically experience polyuria (frequent urination), they will become increasingly thirsty (polydipsia) and hungry (polyphagia).
 Some people may be able to control their type 2 diabetes symptoms by losing weight, following a healthy diet, doing plenty of exercise, and monitoring their blood glucose levels. However, type 2 diabetes is typically a progressive disease - it gradually gets worse - and the patient will probably end up have to take insulin, usually in tablet form.
Some people may be able to control their type 2 diabetes symptoms by losing weight, following a healthy diet, doing plenty of exercise, and monitoring their blood glucose levels. However, type 2 diabetes is typically a progressive disease - it gradually gets worse - and the patient will probably end up have to take insulin, usually in tablet form.